Country Profile Background
Nigeria’s current intergovernmental structures and systems were established in 1976 with the objective of rebuilding democracy from the grassroots up. Although state and local governments have considerable discretion over public service delivery, it has proven difficult to put in place effective accountability arrangements, to improve the quality of democratic space, and to improve the economic opportunities of Nigeria’s 150 million people. This is in part due to the systemic challenge posed by a governance system that is financed almost exclusively from oil revenues which all levels of government share.
 Organizational/Governance Structure of the Public Sector
Organizational/Governance Structure of the Public Sector
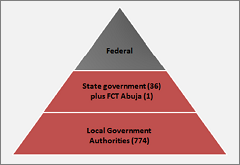
Nigeria is a federal republic which is organized around three democratically elected levels of government: federal (central), state and local. Nigeria’s 36 states range in population size from roughly 2 million to 9 million people. Below the state level, local governments exists in a single tier across all states. There are 774 local government authorities (LGAs). The constitution guarantees a system of local government run by democratically elected councils, and requires all states to enact legislation providing for the establishment, structure, composition, finance and functions of local government councils.
Functional Responsibilities of the Local Public Sector
The 1999 Constitution assigns functional responsibilities to the federal, state and local levels. The Second Schedule of the Constitution identifies both exclusive powers of the federal government (including defense and police) as well as numerous areas of concurrent federal and state power. Powers not specifically assigned belong to the state level. Similarly, the Fourth Schedule of the Constitution identifies a number of exclusive functions of local government councils, while further identifying that local councils have responsibility for participating in the delivery of primary education, health services, and the promotion of agriculture within their state.
 Fiscal Profile of the Public Sector
Fiscal Profile of the Public Sector
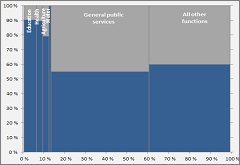
Local public sector expenditures account for 61.3% of total public spending in the Nigeria, while the central public sector retains 38.7% of public spending for functions outside the local public sector. Although local government authorities are the government level that is closest to the people, LGAs account for only 16.1% of public spending. In contrast, state governments account for 38.3% of all public spending. In addition to state and local government spending, the federal government allocates 7.0% of total public expenditures for activities and functions that are part of the local public sector (including police, agriculture, health, universal basic education and higher education).
State government and local government authorities in Nigeria are highly depending on intergovernmental fiscal transfers. Unconditional, formula-based allocations from the Federal Account, VAT revenue sharing, and other oil revenues accounts for almost two-third (63.8%) of state revenues. Earmarked transfers account for an additional 12.2% of state finances. In contrast, own source revenues account for only 24.0% of state financial resources. Grant dependency is even greater at the local level, where 99% of all financial resources comes from intergovernmental fiscal transfers.
 Institutional Profile of the Local Public Sector
Institutional Profile of the Local Public Sector
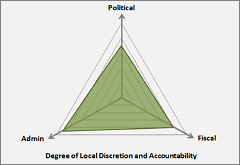
State governments in Nigeria have a high degree of autonomy and discretion in conducting their political, administrative and fiscal affairs. However, the size of state jurisdictions and the limited degree of funding from own revenue sources makes it difficult for residents and communities to hold state level officials accountable. In turn, state governments exert considerable influence over local government authorities within their jurisdiction. For instance, LGAs have only modest authority over their own personnel, as all local staff above supervisory grade is employed by state-level Local Government Service Commissions, while local teachers are employed by state controlled Local Government Education Authorities.
Country Profile Information
Complete LPS Country Profile: Nigeria (PDF)
Complete LPS Country Profile: Nigeria (XLS)